Petroleum is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds that are found in geological formations beneath the Earth’s surface.
The name Petroleum covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crude oils and petroleum products that are made up of refined crude oil. A fossil fuel, it is formed when large quantities of dead organisms, usually zooplankton and algae, are buried underneath a sedimentary rock and undergo intense heat and pressure. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling. This comes after the studies of structural geology (at the reservoir scale), sedimentary basin analysis, reservoir characterization (mainly in terms of porosity and permeable structures).
It is refined and separated, most easily by boiling point, into a large number of consumer products, from petrol (or gasoline) and kerosene to asphalt and chemical reagents used to make plastics and pharmaceuticals.
Petroleum is used in manufacturing a wide variety of materials, and it is estimated that the world consumes about 88 million barrels each day.
Composition of Crude Oils
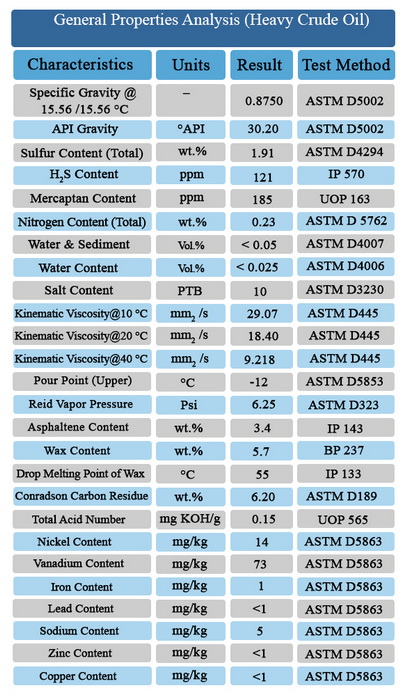
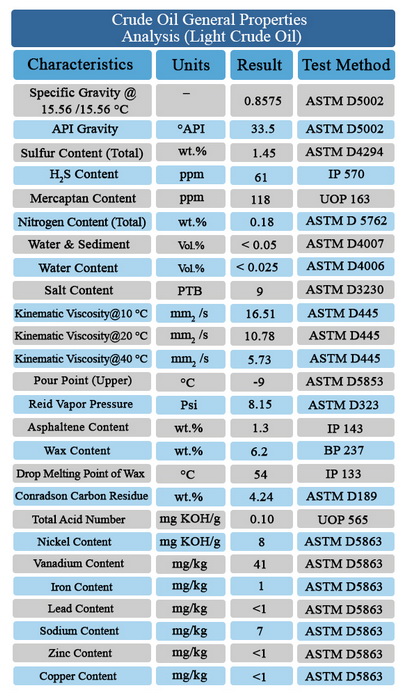
Crude oil (petroleum) is a naturally occurring brown to black flammable liquid. Crude oils are principally found in oil reservoirs associated with sedimentary rocks beneath the earth’s surface. Although exactly how crude oils originated is not established, it is generally agreed that the crude oils derived from marine animal and plant debris subjected to high temperatures and pressures. It is also suspected that the transformation may have been catalyzed by rock constituents. Regardless of their origins, all crude oils are mainly constituted of hydrocarbons mixed with variable amounts of sulfur, nitrogen, and oxygen compounds. Metals in the forms of inorganic salts or organometallic compounds are present in the crude mixture in trace amounts. The ratio of the different constituents in crude oils, however, varies appreciably from one reservoir to another.
Normally, crude oils are not used directly as fuels or as feed stocks for the production of chemicals. This is due to the complex nature of the crude oil mixture and the presence of some impurities that are corrosive or poisonous to processing catalysts.
Crude oils are refined to separate the mixture into simpler fractions that can be used as fuels, lubricants, or as intermediate feedstock to the petrochemical industries. A general knowledge of this composite mixture is essential for establishing a processing strategy.
Comments Off on Crude oil with 103 visit